简介
归并排序(Merge Sort)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效,稳定的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
一般步骤
1. 二分递归法-分治法
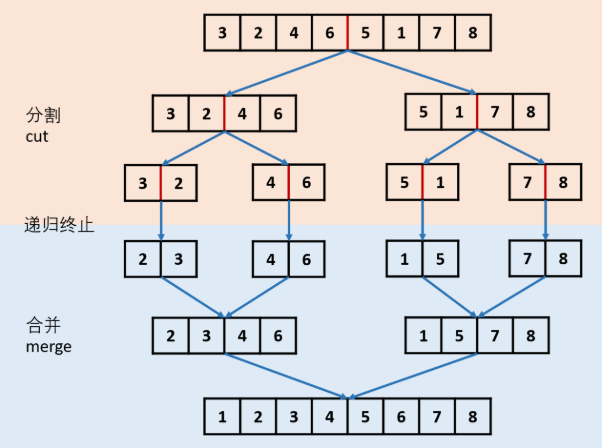
2. 线性迭代
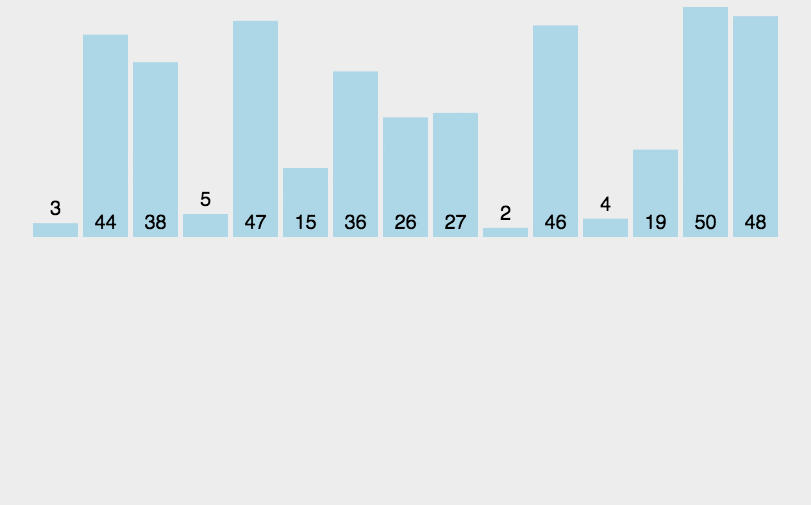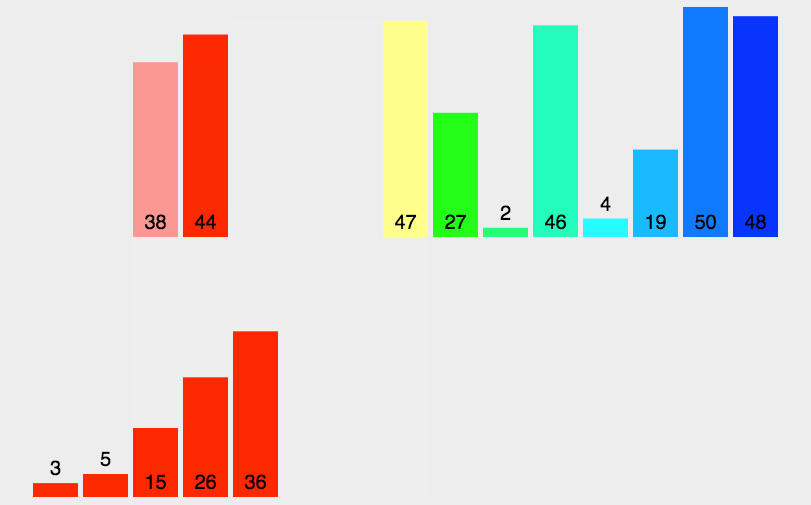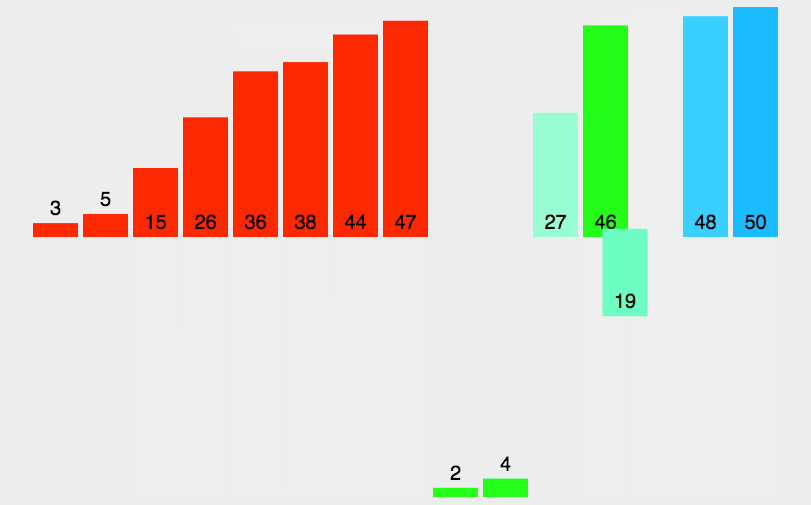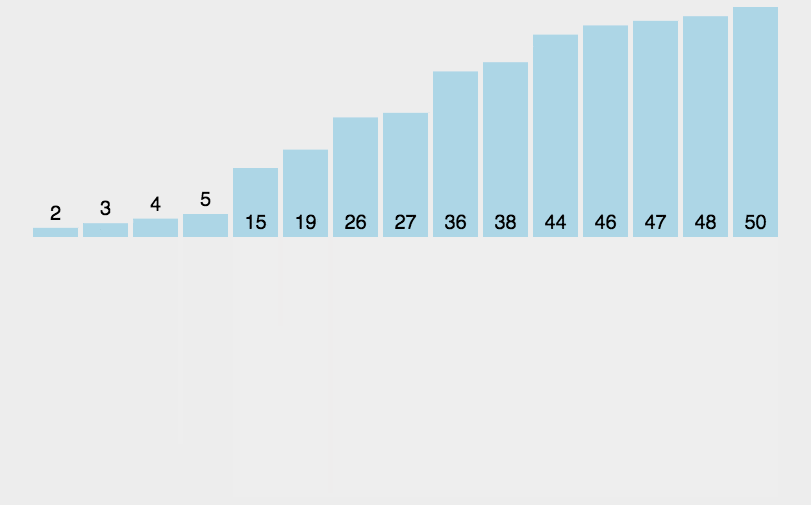
示例代码
链表排序,采用二分递归
// 采用归并排序
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 递归基!!!
// 若head 为空 或者为 单个节点则返回自身。
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
// 找中点
ListNode middle = findMiddle(head);
ListNode tail = middle.next;
// 分隔成两个链表
middle.next = null;
// 分而治之!!!
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(tail);
// 合并子问题 将两个升序链表合并成一个升序链表
ListNode res = mergeTwoLists(left, right);
return res;
} private ListNode findMiddle( ListNode head){
// 采用快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
} private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2){
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode node = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
node.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
node.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
// 若l1剩余
if(l1 != null){
node.next = l1;
return dummy.next;
}
// 若l2剩余
if(l2 != null){
node.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
}
// 若 l1 和l2 同时为空, 则 只会在初始输入两者均为空时发生。
// 所以直接返回为空
return null;
}